SEO
In our daily lives, we use Google to find answers to everything we can think of. From the results of a football match to the causes of headaches or the healthiest recipes for dinner.
In fact, Google is the most popular search engine in the world, controlling 92.2% of the market , well ahead of Bing (2.8%) and Yahoo (1.51%). It is estimated that more than 60,000 searches are made on its bar per second.
This represents a great potential for your company, because behind each of these searches there could be a potential client. Therefore, in this article we will explain everything you need to know to appear in the first results of search engines thanks to SEO. Take note!
What is SEO?
SEO ( Search Engine Optimization ) is a practice aimed at increasing the quantity and quality of visits that a website receives. It involves applying a series of optimization strategies and techniques to ensure that a site's web pages appear in the first results when a user performs a search on the Internet.
Among these strategies and techniques, there are internal and external factors, such as optimizing the website structure, content, keywords, performance, links, user experience, and even domain authority in search engines.
History of SEO
There is no clear consensus on the origin of SEO. Many argue that it was born in 1991 with the first web page. For others, its origin dates back to 1994 with the creation of WebCrawler , the first bot that indexed web content; and Lycos , the first search engine that used a page crawling system.
According to specialist Danny Sullivan , founder of Search Engine Land , the term Search Engine Optimization was first used in 1997 by John Audette and his agency, Multimedia Marketing Group. However, the techniques used under that name at that time were very different from those used today. At that time, keyword density was the main factor in search engine ranking. For this reason, many webmasters abused the use of keywords to appear on the results pages, but their content was often not useful to users. Thus, the need arose to develop more complex ranking algorithms capable of ranking websites, taking into account other factors that webmasters could not manipulate so easily.
In 1998, Google entered history with the aim of delivering a better user experience through a more developed algorithm that rewards quality content with better web positioning and visibility.
Over the years, Google has maintained that belief. If the experience it offers is good, users will continue to choose it over other search engines. That's why it constantly makes changes to its algorithm, with Panda (2011) and Penguin (2012) being some notable updates .
With Panda , he focused on evaluating the quality of sites and penalizing those that copied information from other sites . He also began to take into account factors such as the number of visits, bounce rate, time spent on the site, and frequency of updates. With Penguin , he sought to encourage organic link building and penalize sites that tried to position themselves using links that did not provide value to the user.
The history of SEO will continue to be written every day. According to various experts, Google makes more than 500 updates to its algorithm every year. Most of the time the changes are imperceptible, but other times they have a great impact on positioning and force all web administrators to update themselves.
SEO Strategies
Now that you know what SEO positioning is, it's time to learn about the strategies used in this discipline. They are mainly classified into two types:
White Hat SEO
It covers those methods and techniques that comply with the ethical standards of search engines. It consists of positioning a website through content that provides value to the user. Generally, these are strategies that achieve positive results in the medium and long term.
Some examples of good practices are:
- Create relevant, quality content that responds to users' search intent
. - Write descriptive meta descriptions and title tags
. - Include internal links in articles and landing pages to improve navigation and user experience on the website
. - Avoid leaving orphan pages , as they can be difficult for users and search engines to find
. - Use quality and relevant external links to increase the authority of the site
. - Implement a friendly and easy-to-understand URL structure
. - Optimize website loading speed and user experience
. - Include alternative texts or alt texts in the images on the website.
Black Hat SEO
This refers to practices that aim to position a website using techniques that go against search engine standards. Their sole objective is to appear in search results, without taking into account the needs and experience of the user. These are risky strategies with little chance of being maintained in the long term.
Some examples of bad practices are:
- Stuffing website pages with keywords in an excessive and inconsistent manner in an attempt to trick search engines. This is known as Keyword Stuffing
. - Creating pages specifically to trick search engines, attract traffic and redirect users to other pages. These pages are known as doorway pages
. - Publishing content copied exactly from other websites, without providing any extra value, to obtain better positioning
. - Paying other websites to include a link to a particular page, with the intention of increasing its authority
. - Posting hidden texts (such as white text on white backgrounds) with lots of keywords to trick search engines.
Furthermore, depending on the internal or external tasks being performed, search engine optimization can also be classified as follows:
SEO On page
This refers to all those measures that can be applied internally so that search engines can crawl and interpret your website optimally. For example:
- Improvements in the quality of information , content, structure, organization, level of development, depth of information, indexability to sources and audiovisual resources
. - Improvements in usability, refers to good site development, intuitive web design, good loading speed and adaptability to mobile devices
. - Technical factors such as optimization of meta tags, headers, rich data, content hierarchy and good URL formatting.
SEO Off page
It is much more related to external factors . It involves taking actions to improve the authority of your domain. Variables such as:
- The quantity and quality of inbound links . That is, of websites that link to you on their portal (the official term is Link Building).
- Presence and activity on social networks
. - Geographic location . A website may be more relevant to users living in one geographic area than another. For example, if a person searches for “how to pay taxes,” they are likely to want to read information about their country.
Difference between SEO and SEM
Both SEO and SEM ( Search Engine Marketing ) have the same goal, which is to show up at the top when a user performs a search. However, there is a big difference between them:
SEO is organic positioning
As we have seen, it consists of applying strategies, both inside and outside a web page, to appear in the organic results of the Search Engine Results Pages (SERPS), gaining traffic and relevance on the web in the medium or long term.
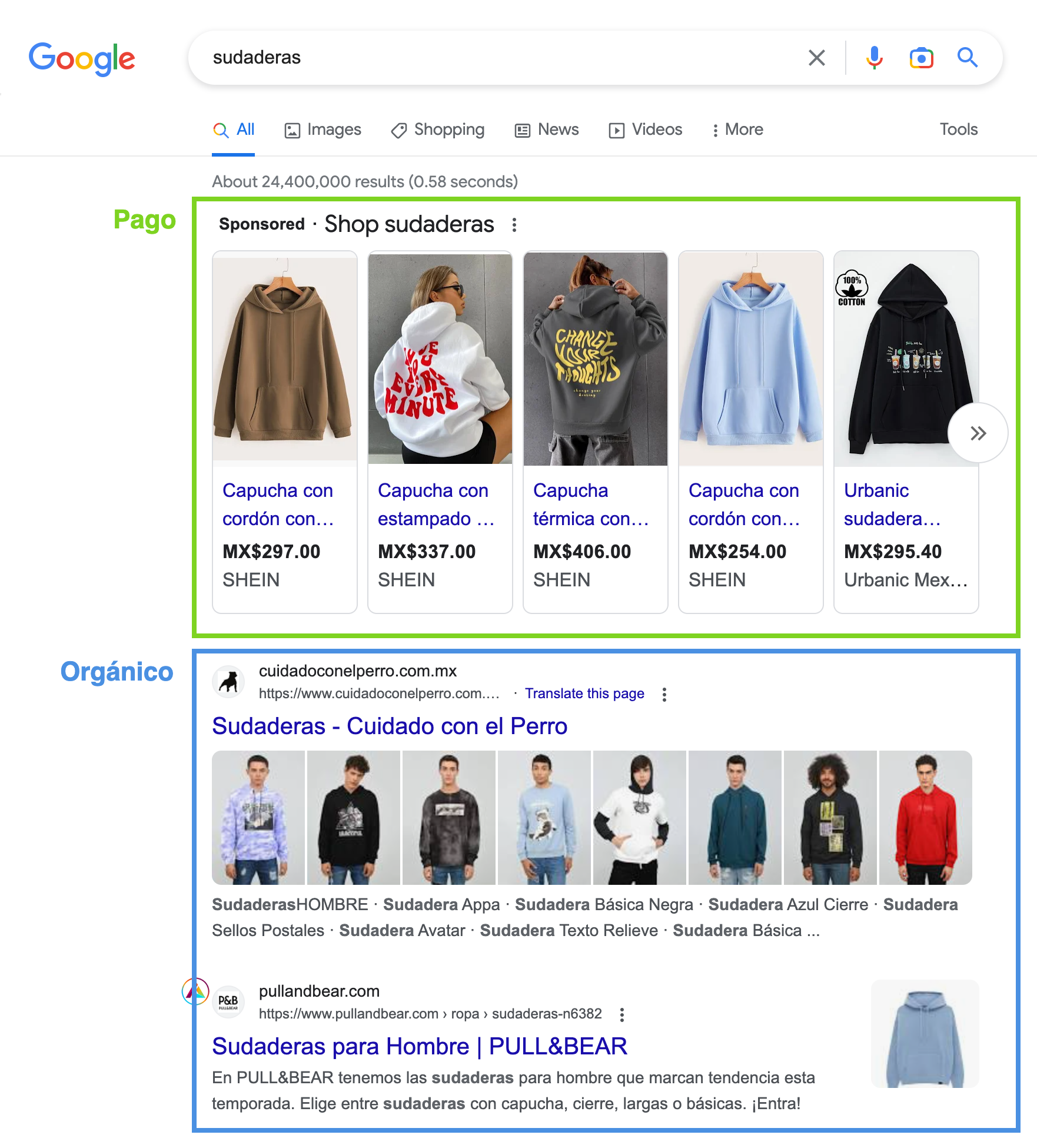
SEM is paid positioning
It allows you to gain immediate visibility and traffic by implementing paid advertising campaigns for specific keywords. For example, if you have an online clothing store, you can pay Google through Google Ads (formerly Google Adwords ) so that every time a user types “sweatshirts” into the search engine, your ad appears in the first results.
How do search engines work?
To achieve good web positioning, it is important to understand how search engines work. They are based on two processes:
Tracking
The first process of a search engine is to crawl websites using computer bots (e.g. Googlebot ), which are often known as " spiders . " These bots visit a website, collect information, and identify links. They then click on those links just as a user would. In this way, they move from page to page to discover new content .
This would be the basic operation of this process. However, it is essential to mention that bots do not always crawl pages in the order in which they discover them, but rather they prioritize some over others, taking into account some factors such as: whether it is new or not, the PageRank of the URL or how often the URL changes.
Indexing
After crawling the pages, the bot stores all the content in a database. From there, a large index is formed, which will be displayed when a user performs a search.
But how are the results sorted in this index? This is where search engine algorithms come into play .
There are billions of search results for “ digital marketing ” but search engine algorithms are tasked with showing users, in fractions of a second, the pages they consider best or most relevant to their search intent in the top positions.
To determine this relevance, the algorithms take into account various variables. According to experts, Google has more than 200 positioning factors and although no one knows them all exactly, it is known that some of the most important are:
- The authority of the site on a given topic.
- The quality of the content and its timeliness.
- The loading time of the website.
- The quantity and quality of backlinks.
- The level of mobile optimization.
Types of search intent
One of the key aspects to achieve good organic positioning in search engines is to know how to identify and take into account the intention behind each search that a user performs. What results do they expect to find? What are their needs or expectations?
When a user types “soccer ball” into the Google search bar, he or she is probably expecting to find a product offering in the results . He or she may intend to view different models, compare prices or features, and buy. Whereas, if he or she types “history of the soccer ball,” he or she has an informational need.
Understanding search intent is important to objectively respond to user questions and needs and attract the right audience to a website.
Below we explain three types of search:
- Navigational search: This occurs when the user searches for a specific website or brand. The user is already familiar with the brand, but may not remember the exact URL to access it.
- Informational search: This is when the user searches for information on a specific topic or question because they want to learn more. For example, when someone searches for “ What is Inbound Marketing ” they are doing an informational search .
- Transactional search: In this search, the user wants to carry out a transaction, such as: hiring a service or making an online purchase.
Benefits of SEO
There are millions of websites and online stores that receive no more than 100 visitors per month. Using platforms such as Webflow or WordPress, anyone can create a website without being a webmaster. However, for it to be truly successful, it needs to be constantly optimized.
By implementing SEO techniques and strategies, it is possible to achieve great benefits, such as:
- Increase visibility and traffic : More than 25% of people click on the first search result on Google. This means that if you manage to rank your site in the first place for a keyword with more than 50,000 searches per month, you would have at least 12,500 monthly visitors
. - Get more leads: As part of an Inbound Marketing strategy, SEO is a great tool to convert site visitors into leads and, subsequently, into customers
. - Stand out from the competition: If you are consistent, create quality user-focused content, and make all the necessary technical optimizations on your website, you will have a significant competitive advantage
. - Build loyalty: Users tend to trust Google's results. Therefore, if your website appears among the top positions, people will be more open to trusting your brand and, with a good content marketing strategy , it will be easier for you to convert them.
Advantages of SEO for startups
Search engine optimization practices are useful for any business. However, for startups they may be even more necessary, as these are new or young companies that usually compete with already established and long-standing companies. Good organic positioning is key for them to achieve:
- Make yourself known and get new clients without having to invest large amounts of money.
- Build and maintain a brand image.
- Differentiate yourself from competitors.
- Increase your growth and accelerate your expansion.
In conclusion, startups that consider SEO strategies from the beginning, in their business plan, are more likely to achieve good results.
SEO Terms You Need to Know
If you are just starting to take your first steps in this world of search engines and positioning, we share with you a glossary with 15 terms that will help you understand everything a little better:
- Google Algorithm : set of mathematical formulas (in this case from Google), which are responsible for determining and establishing the positions of each of the millions of websites.
- Web spider: Also known as crawler, bot or search robot, is an automated program used by search engines to collect information from websites. They navigate websites by following links and collecting information about content, keywords, structure and other aspects relevant to indexing.
- Web architecture: is the structure and hierarchy of a website. A good web architecture makes it easier for search engines to crawl and index all web pages and allows users to navigate and perform actions on the website easily.
- Backlinks : also known as inbound links , are links that point to our website from other pages.
- Crawling: is the process by which search engine robots track, evaluate and classify the content of websites, with the aim of displaying it as a search result.
- Domain Authority: a measurement system patented by the Moz tool , to add value to the relevance and authority of a domain. Although it is well known, it is not always correct or accurate, so it is recommended to compare its results with other data.
- Keywords: These are terms that users use when searching on the Internet. They can contain one or more words (the latter are known as “ Long-Tail Keywords ”). When used strategically on a website, better positioning can be achieved.
- Landing Page: This is a page created specifically with the goal of converting visitors into leads or potential customers.
- Link Building : is a set of techniques and actions that seek to generate external links that redirect to your website to increase the authority of a website.
- Meta Description: This is the SEO description of the page, which summarizes the content of the web page. This is found below the title of the website on the Google results page. Using this text strategically can draw the reader's attention to your site and increase organic visits.
- Meta Title: This is the title of the web page. This tag is extremely important, as it is one of the main factors taken into account by bots and web spiders in their data categorization process.
- Page Authority: This is a metric created by Moz to evaluate the ranking of each page in search engines. Unlike Domain Authority, which measures the relevance of a domain as a whole, this one evaluates the ranking of each page individually.
- Sitemap: As the name suggests, it is a map of a website. It makes it easier for bots to crawl all of your pages, making indexing processes faster and more efficient. You can build your sitemap with different tools .
- SERP: stands for Search Engine Results Page and refers to search results pages .
- Webmaster: is the professional in charge of creating and maintaining a website. He or she must have knowledge of web design, programming languages and other technical aspects, as well as keep up to date with the latest digital trends.
5 SEO tools: advantages and disadvantages
We present you 5 of the most useful and necessary tools in a search engine optimization process:
1. Google Analytics
Google Analytics is an essential tool. It allows you to monitor the performance of your website in real time or over certain periods of time. Through it, you can identify which are the most visited pages within your site, from which devices or cities they visit you, what is the bounce rate or how much time users spend on it, the conversion rate, etc.
2. Google Search Console
Google Search Console is another free service offered by Google that can be integrated with Analytics. It helps you monitor, maintain, and troubleshoot your website by allowing you to understand and improve the way Google views your site. It also notifies you and generates reports on your status in processes such as indexing, web pages that redirect to yours, possible SPAM problems, and much more.
3. MozBar
MozBar has some great features for measuring On Page SEO factors. It shows you factors like MozRank, Page, and Domain Authority for both your website and others. This is useful if you want to do market and content analysis. It also provides extremely useful information about external or internal links and key terms.
4. Screaming Frog SEO Spider
Screaming Frog audits links, images, CSS and many other technical aspects of a site. It generates a report showing what a web spider sees when crawling. It is one of the most popular tools worldwide for performing audits.
5. Semrush
Semrush allows you to analyze competitor websites and strategies, revealing aspects such as keywords, paid advertising, and links from other websites. It also generates optimization suggestions for On-Page SEO and technical factors such as Crawl and Page Audit, among many other functions.
There are many factors that influence website positioning. Therefore, if you want to always be on the first page of results, the list of tasks is long. From performance analysis and competition studies to constant monitoring of technical factors and the creation of quality content.
All of this can be overwhelming when you don't have enough knowledge. If this is your case, it is ideal to have an SEO agency that can accompany you in the process.